

- Wxhexeditor little endian Patch#
- Wxhexeditor little endian software#
- Wxhexeditor little endian windows#
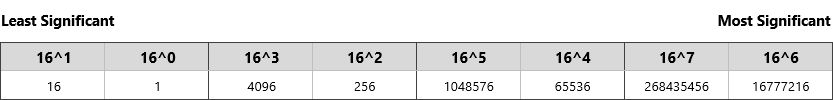
We write decimal numbers and binary numbers with the highest non-zero coefficient on the left and the lowest on the right. Likewise, a binary number like 10110 is shorthand for 1 * 2 4 + 1 * 0 3 + 1 * 2 2 + 1 * 2 1 + 0 * 2 0. That is, each numeral is multiplied by a power of ten according to its position in the number. When you write a decimal number like 42357, that is shorthand for 4 * 10 4 + 2 * 10 3 + 3 * 10 2 + 5 * 10 1 + 7 * 10 0. I will also examine only unsigned integers, since that makes it easier to explain the differences between big and little endian and other byte-orderings. (See Computer numbering formats for the differences between integer, fixed-point and floating-point numbers.)įor purposes of this post, I will discuss 32-bit (4 byte) integers, though the same concepts will clearly apply to both smaller and larger representations. For instance, many modern processors have functional units devoted to floating point operations that process data in larger chunks than the integer-based functional units. The maximum number of bytes that can be grouped together and handled as a unit by a CPU varies by the type of processor, and may in fact vary in different functional units in the same computer. This clearly does not handle large enough numbers for many problems, so groups of bytes are used to represent still larger numbers. You can read more about the various representations of signed numbers at Wikipedia. This can be either an unsigned number from 0 to 255 or a signed number from -128 to 127, at least using the most common number representation, "two's complement".
Occasionally, you will also hear of half-byte entities (four bits), naturally termed "nibbles".Īn eight-bit byte can represent 256 values (2 8). Modern computers, to my knowledge, all use eight-bit bytes, though I am fairly certain that some older computers used other sizes. Bits, in a fit of cleverness, are organized in groups called "bytes".

Ĭomputers store numbers as a sequence of binary digits, or "bits". Update: I am post-dating this to move it to the top of the first page. As a bit of penance, this post is for those people who find their way here by searching for information on endianness. I did not anticipate, though I certainly should have, that this choice would cause people searching for information on big- and little-endianness to find this blog, where I am sure they have not found what they are looking for.
Wxhexeditor little endian software#
The most frequent scenario for any competitive hexeditor will be: I'm sitting here and waiting but never get the result.When I first created this blog, I chose the title as sort of a whimsical phrase that reflected my life as a software developer, even though I had no plans to discuss software in this blog. For example, if you try to search and replace text/hex/decimal/binary data pattern in 1GB - 1TB file, you'll simply find no competitors for our product.
Wxhexeditor little endian Patch#
This free binary file editing utility also provides you with the following features: Unlimited Undo/Redo GoTo Offset Save/Load Operation History 32bit/64bit Patch Creation Find/Replace for hex/decimal/octal/float/double data and binary codes Grouping by Bytes, Words, Double Words, Quad Words įreeware Hex Editor Neo is extremely useful for viewing, modifying and analyzing hexadecimal data in extra large files and disks. You may also exchange binary hexadecimal data with other applications through the Clipboard. Overwrite and insert modes are supported. You may extensively use the following basic functionality: Type, Cut, Copy, Paste, Fill, Delete, Insert, Import and Export and even try some advanced functionality. It's distributed under "Freemium" model and provides you with all basic editing features for free.
Wxhexeditor little endian windows#
Free Hex Editor Neo is the fastest large files optimized binary file editor for Windows platform developed by HHD Software Ltd.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
